How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained
A transition metal is a chemical element that has a partially filled d orbital. The lanthanides and the actinides at the bottom of the table are sometimes known as the inner transition metals because they have atomic numbers that fall between the first and second elements in the last two rows of the.

Transition Metal Definition Properties Elements Facts Britannica
These elements form coloured compounds and ions.

. Properties of transition elements are discussed below. However in the transition metals moving left to right there is a trend of increasing atomic radius which levels off and becomes constant. However they are also considered as transition metals because they have similar properties to those of transition metals.
These elements all of which are metals include some of the best-known names on the periodic table iron gold silver copper mercury zinc nickel chromium and platinum among them. The properties of the elements of the first transition series differ from those of the heavier transition elements in many ways. Form stable complexes Have high melting and boiling points Contain large charge radius ratio Form compounds which are often paramagnetic Are hard and possess high densities Form compounds with profound catalytic activity Show variable oxidation states.
This colour is explained by the d-d transition of electrons. 1Definition of Representative Element. They usually combine to form coloured compounds.
The general properties of the transition elements are as follows. These properties of the transition elements are listed below. For example elements on the left in groups 1 2 and 13 are going.
Filling Transition Metal Orbitals. In general the next higher s sublevel is already filled or has one electron missing. We know that electronic configurations of transition elements is invariably n-1d 110 ns 0 or 1 or 2 which indicates that i the electronic configurations of transition elements differ from one another only in the number of electrons in d orbitals in the n-1th shell and ii the number of electrons in the outermost shell ns is invariably 1 or 2.
Trends in the metallic characteristics of the transition elements on the other hand can be seen. There is a relatively low gap in energy between the possible oxidation states of these elements. Most transition metals are grayish or white like iron or silver but gold and copper have colors not seen in any other element on the periodic table.
They tend to crystallize and are generally good conductors of heat and electricity. Because the main group elements consist of both metals and nonmetals their physical properties are going to be quite different. A number of other transition elements are probably somewhat.
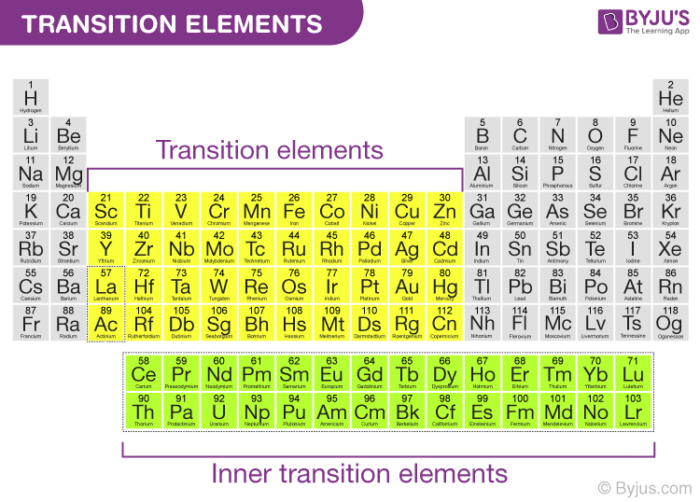
They are the Lanthanides and the Actinides. Properties of Transition Elements The transition elements general properties are as follows. They have very high melting points and boiling points.
In the periodic table of. This only applies to the first row transition metals adjustments will be necessary when writing the electron configuration for the other rows of transition metals. The transition elements therefore exhibit many oxidation states.
The d10 metals namely Zn Cd and Hg have completely filled d -orbitals. Many transition element compounds are brightly colored due to the inner-level d electron transitions. Compared to other metals most transition metals have.
Transition metals have typical metallic qualities such malleability ductility high tensile strength and metallic lustre. The transition metals as a group have. Transition metals look shiny and metallic.
Inner transition elements are in the f-block and in the f-orbital have valence electrons. These elements are characterized by having unfilled d sublevels. Metels in transition elements are very good conductors of heat and electricity.
High melting point group 1 metals have low melting points hard group 1 metals are soft high density group 1 metals have lower densities Chemical properties. What are the properties of the transition elements. The transition metals are malleable easily hammered into shape or bent.
The three main differences are. These metals tend to be very hard. The transition elements are found in groups IIIA-IIB new groups 3-12.
The physical and chemical properties of transition elements differ from the main group elements s-block. In the transition elements the number of electrons are increasing but in a particular way. I The atomic sizes of the elements of the first transition series are smaller than those of the heavier elements of 2nd and 3rd transition series.
Typically when moving left to right across the periodic table there is a trend of decreasing atomic radius. They are frequently paramagnetic. Quick Summary of the Transition Metal Properties Low ionization energies Positive oxidation states Multiple oxidation states since there is a low energy gap between them Very hard Exhibit metallic luster High melting points High boiling points High electrical conductivity High thermal conductivity Malleable.
They can form several states of oxidation and contain different ions. They have a variety of oxidation states. The difference between representative elements and transition elements is that representative elements are the chemical elements in the group 1 group 2 and in the groups from 13 to 18 whereas transition elements are chemical elements in group 3 to group 12 including Lanthanides and Actinides.
Densities and Metallic Radii The density and hardness of transition elements are high due to the small size of their atoms and the strong metallic bonding. The transition elements are in the d-block and in the d-orbital have valence electrons. They are typically metals with a high melting point.
The transition elements are the elements that make up Groups 3 through 12 of the periodic table. The ability to become magnetic temporarily in. They have a high chargeradius ratio.
The electron configuration for the first row transition metals consists of 4s and 3d subshells with an argon noble gas core. In other words they have d1 to d9 electrons. High density and hardness.
The key difference between first second and third transition series is that the outermost d orbital of first transition series elements is 3d while the outermost d orbital second transition series is 4d and the outermost d orbital in third transition series is 5d. Some properties of transition elements are different from those of the metals in group 1. Transition metals are the d -block elements and they have incompletely filled d -orbitals.
The transition metals are the metallic elements that serve as a bridge or transition between the two sides of the table. The biggest difference in properties however is transition metals paramagnetic property. The noble gas before the first row of.

Lesson Explainer Electronic Configurations Of Transition Metals Nagwa

Transition Metals Chemistry Learner
No comments for "How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained"
Post a Comment